Takex TXF-20TDM Wireless Beam with 20-metre external detection.
Contents
The TXF-20TDM is a battery-operated 20-metre twin-beam detection solution designed for rapid deployment in multiple applications.
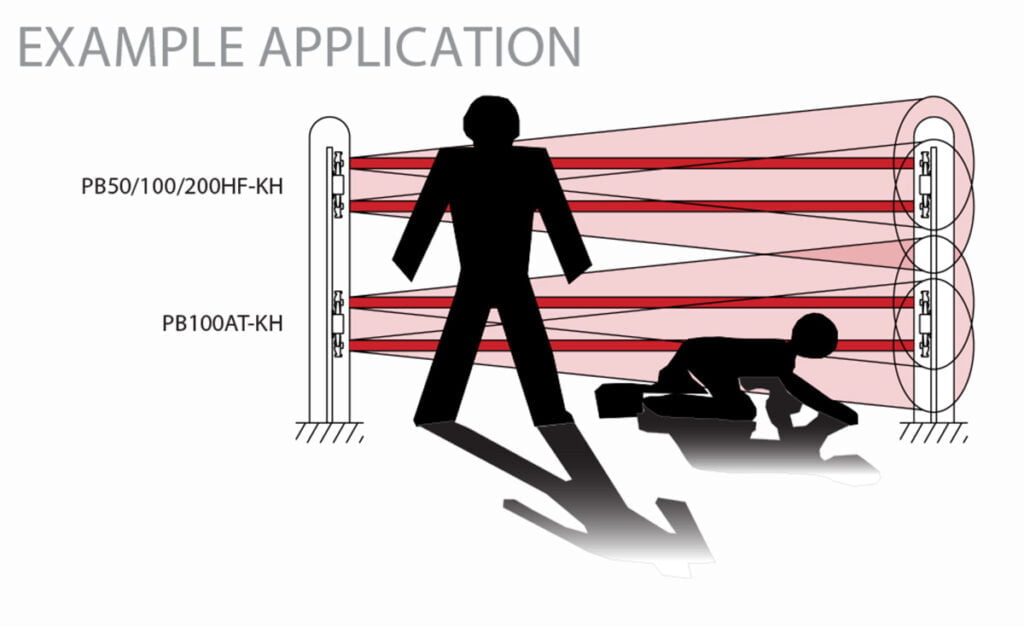
The detection system is a near-infrared pulsed beam interruption system (TR-RE 2 beam simultaneous interruption) comprising 2 synchronised high-power IR beams (with 4 selectable beam channels). Function sound checks are activated for monitor jack, low battery indication, battery saving, and repeat output.
The unit features double modulation technology for enhanced rejection of direct and reflected sunlight, vehicle headlights and other light sources. Making commissioning easier, a red alarm LED shows when an alarm is generated, while a red attenuation LED is displayed when the beam is attenuated – both are active only when the cover is open.
Takex TXF-20TDM Twin Beam sensor is designed for compatibility with leading wireless systems, our battery-operated TXF-20TDM is ideal for rapid deployment; creating temporary or permanent secure intrusion detection systems without costly civil engineering groundworks.
The sensor has a battery life of up to 3 years using 4 x lithium (3.6V 17Ah) batteries and features an IP55 housing that makes it resistant to dust ingress, as well as resistant to low-pressure streams of water. The operating temperature range is -25 to 60C.
Featuring ±95-degree horizontal and ±10-degree vertical optical head adjustment, TXF-20TDM includes a drip-proof housing designed to channel precipitation away from the face of the beam, optional anti-bird spikes, a sound check function for easy alignment, and lightning surge protection.
The transmitter weighs 500g excluding batteries), while the receiver weighs 520g and colour options include red and black. The sensor includes solid-state NC and NO switches, along with solid-state Form C.
You can find out more about these amazing sensors here or from your local distributor in ANZ.
Datasheet
TXF-20TDM Wireless Beam Sensor Features:
- 2x Synchronised high-power beams
- Double modulation for increased light immunity
- 4 Selectable beam channels to prevent crosstalk
- Up to 3 years battery life using 4 x LS33600 (3.6V 17Ah) batteries
- ±95° horizontal and ±10° vertical adjustments
- Compatible with numerous wireless transmitter units
- IP55 Housing.
“TXF-20TDM Wireless Beam with 20-metre external detection.”

How does a wireless beam work?
Passive infrared (PIR) sensors use an active infrared transmitter and receiver located at either end of the external perimeter being protected. If the beam is broken, the loss of signal is interpreted by the receiver as an alarm event and is reported to the control panel for transmission to a monitoring station for response.
What is the difference between active and passive infrared sensors?
Active IR beams act as narrow line crossing perimeter sensors, making them ideal for use adjacent to walls or on rooftops, as there’s no signal spill. Passive infrared (PIR) sensors only detect infrared radiation from the environment. Passive infrared sensors detect intrusion because their pyro electric elements generate a small voltage in the presence of environmental IR, which is interpreted as an alarm event when it crosses a given signal threshold.
What are the advantages of the passive infrared sensor?
PIR sensors are small, inexpensive, low-power, easy to use and don’t wear out. For that reason, they are commonly found in appliances and gadgets used in homes or businesses.
What is a passive infrared range sensor?
A passive infrared sensor (PIR sensor) is an electronic sensor that measures infrared (IR) light radiating from objects in its field of view. They are most often used in PIR-based motion detectors. PIR sensors are commonly used in security alarms and automatic lighting applications.
Where is the best location for a passive infrared sensor?
The best place to fit a PIR is in the corner of a room positioned at right angles to foot traffic moving along natural lines of movement. This ensures maximum coverage of the space as the device maps out its grid. Choke-points are the areas in your home with the most traffic. These could be entry doors or hallways.
PIR sensors should be mounted at least 1.2 – 1.9m away from HVAC ducts as rapid-moving air currents or temperature differences may cause false triggering. Sensors with daylight sensing capability should be mounted away from windows and lighting fixtures as the extra ambient light may interfere with sensor operation.
What are some examples of passive infrared sensors?
Examples are security alarms, door openings, automatic lighting switches, vending machines, lift lobbies, etc. They stand out with the advantage of being cost-effective, simple to use, and reliable in most cases. This article explains what PIR sensors are and their working principle.